Selection of Path Routing
Routing is a mechanism of delivery of data packets transmitted from one network to another network. In a router, usually has a routing table that stores information or routing path to be used when there is data transmission through the router. In certain cases to get to a destination, the router has only one gateway, such as a router must have a network that connects many different segments. A simple example can be seen in the following topology: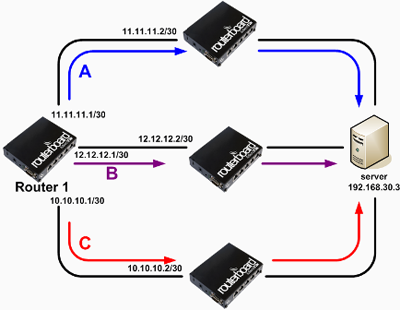
Then how the router determines its route selection?. Which Gateway Router 1 will be used to get to the server?
When there is more than one routing rule, the router has a routing path
calculation mechanisms that will be used routers for data transmission. Routing path selection is based on several parameters: dst-address and the distance of each routing rule.
- First, the router will choose the rule dst-address routing to the most specific.
- Then the router will see the value in the Distance parameter in each routing rule, the smaller the Distance, then the rule will be used.
- If there are multiple routing rule with the same dst-address-specific and the same distance, then the router will choose the Random (round robin).
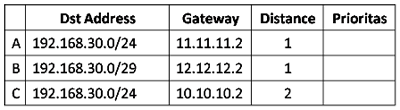
How does the order of priority lanes that will be used Router 1?. We will try to discuss route selection mechanism based router. Keep in mind, traffic is traffic that will be transmitted from Router 1 to the server with the IP address to 192.168.30.3.
Take a look at the routing rule above, for the purpose of IP
192.168.30.3 dst-address = 192.168.30.0/29 more specific than
dst-address = 192.168.30.0/24, so the rule B will be used as a first
priority. Then the rule which will be a priority 2 and 3?.
Consider the rule A and C. Both have the same dst-address - the same /
24, but the value of the distance of the two different rule.
Between A and C routing rule, the router will choose A, because the
distance to the rule parameter value A is smaller than C. It could be
concluded that the rule of the discussion was going to come answer as
follows:
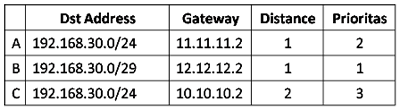
By default distance value is determined according to the type of
routing is applied, for example to Static Route = 1, OSPF = 110, RIP =
120, and so on. However, the value of the distance parameter can also be changed, to make a simple failover mechanism.
An example implementation of a simple failover is when there are two
routing rules with different distance, note the following routing rule:
In these examples, the main route is to go to 192.168.30.0/24 gateway 11.11.11.2.
If the gateway 11.11.11.2 end / die, it will automatically update the
routing rule that will use the router for data transmission will shift
to using the backup path, which is the gateway 10.10.10.2. Network admin not to bother - bother to change the routing table information manually.
No comments:
Post a Comment