User Bandwidth Management Hotspot in Bypass (IP Binding)
Technological developments require that all people have a smart phone digenggamannya, even the day the price of smart phones more affordable by all audiences in Indonesia. Automatically needs of the Internet is increasingly important for many people. No wonder if any crowded places such as offices, hotels, campuses, malls and so provide hotspot service. So many have concluded Wireless Hotspot must be through the media, if you are one of them please read the article below
If you already studied the article at the link we have agreed that in
Mikrotik Hotspot is a system to provide authentication features to the
user that will use the network.
But we can also give privileges to some users that do not need
authentication implementation examples there are more details in the
article below
After Users in bypass, meaning the user is not able to do the bandwidth limitation using the User Profile. To overcome this we can do a number of ways depending IP bindings we do.
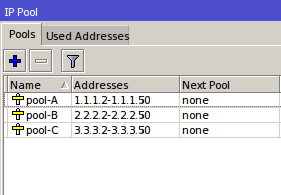
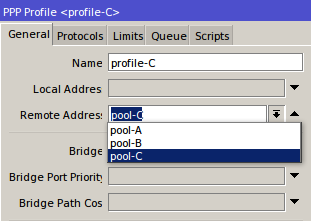
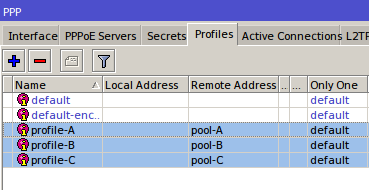
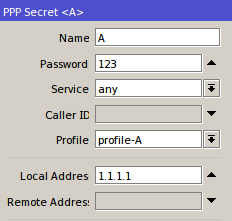
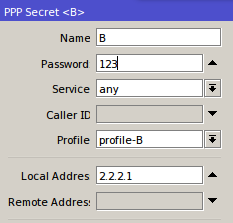
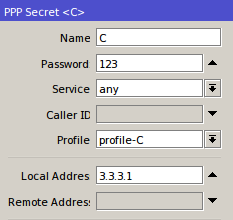
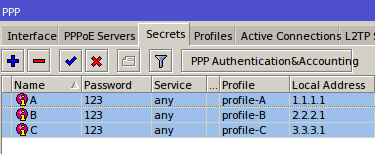
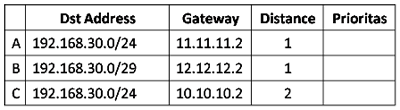
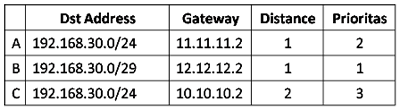
IP Binding by allocating a specific IP
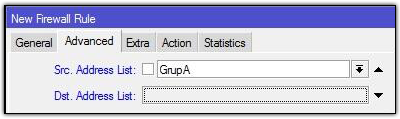
In this method, we will allocate special ip address which will be given to the user bypasses. The ip router will allocate the bypass user based on mac-address, so the ip address user who bypassed unchanged - a fox. Just as making static-lease on a DHCP server settings. Do I go to the menu IP >> >> Hotspot IP Bindings. Then add the Mac Address of the user who will be bypassed and decide to address it.
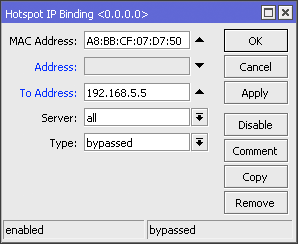
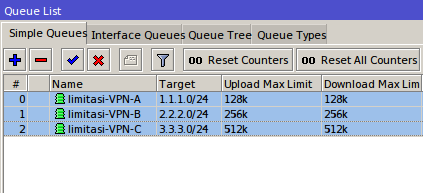
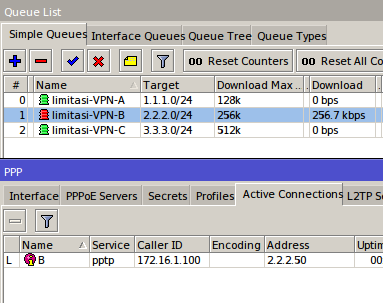
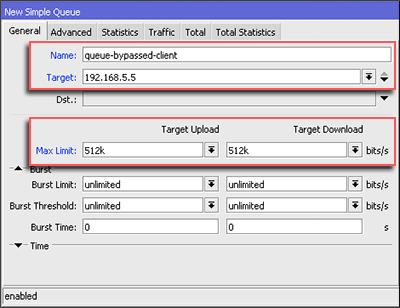
If using this bypass means, to perform management bandiwdth we just add
Simple Queue leading to the IP we have set in to the IP Address
Bindings.
IP Binding without allocation of IP Address
With this method, the user simply bypassed by mac-address user device. Ip address that will didapatakn random user depending on the DHCP server. How to bypass, select the menu Hotspot IP >> >> IP Bindings. Then add the Mac Address of the user who will be bypassed.
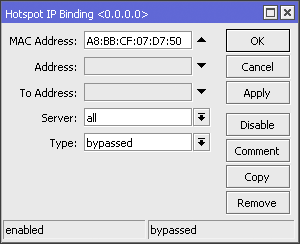
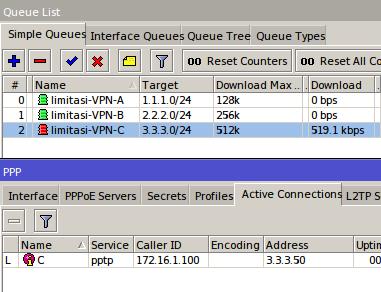
If using bypass this way, to be able to perform user management are
bypassed we should mark the first packets through the router with mac
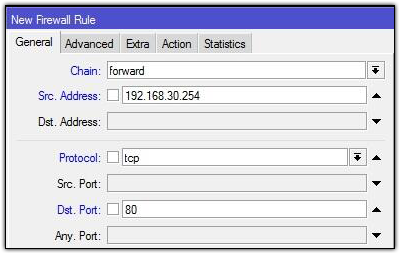
address. We can use the features of Mangle. First we make a mark-conection first: Firewall IP >> >> >> Add Mangle
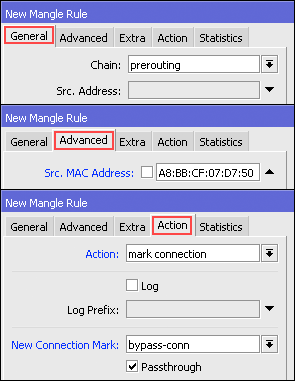
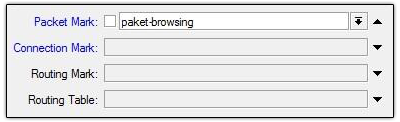
The next step makes Mark Packet based mac-connection that was made
before, via menu Firewall IP >> >> >> Add Mangle
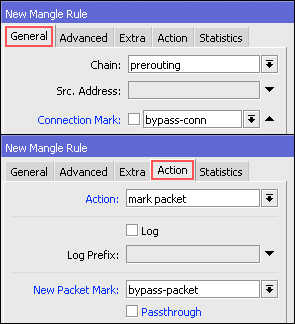
Lastly, we can make a new bandwidth management using the Simple Queue based mark-packet that has been made in the mangle. Do not forget, the parameter "Target" please fill in your hotspot network segment.
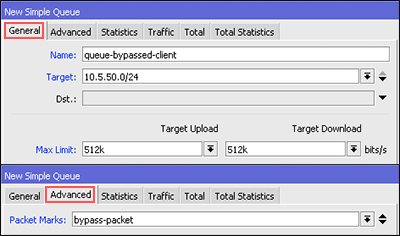
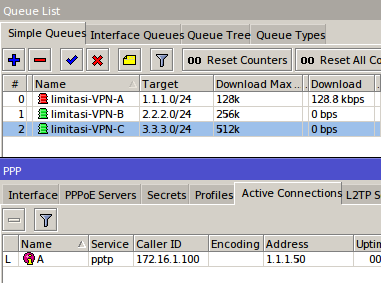
If the above steps are finished, then try to do bandwidth test user side are bypassed. Actually there are many ways you can do for the user management in bypass, like PCQ, static-leases, etc.
Both the above steps are just as simple alternatives that can be used
for bandwidth menagement user who bypassed the hotspot network.