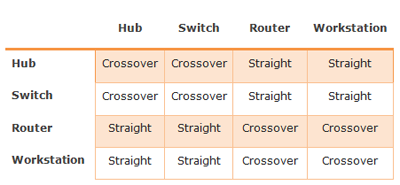
Features Logging In Mikrotik
One feature that is visible on his Mikrotik simple and probably also forgotten but have a fairly important function is LOGGING feature.RouterOS is able to perform a variety of recording information system events and status of the router.
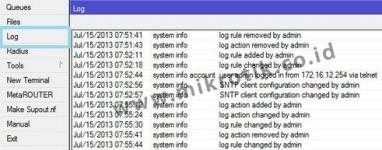
By default RouterOS will keep records of all activities and processes that occur in the router and keeps a record (log) of the RAM. List of record (log) can be seen on the menu / log.
Logs are located in menu / logs will be lost once we restart the router because the log is stored only in RAM.
Examples of the appearance of the menus / log via Winbox.
In network troubleshooting will be more effective by analyzing the logs of the Router prior to knowing what the process is already happening. So it will be easier to map the problem and determine a solution.
Too much information that we get if we just look at the menu / log, so it may be difficult for analysis. For that we can make the topic of what will be recorded and will be stored or displayed where the log.
Besides stored in memory (RAM) routers, logs can also be stored as a file on the storage router, sent via email or syslog server is displayed on the device itself.
This setting can be done in the menu / system logging.
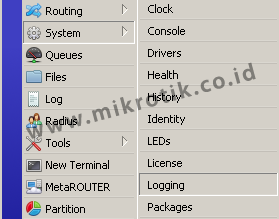
If you notice there are two tabs in the menu / system logging, the Rules Tab and Tab Action.
Tab Action (/ system logging action)
Used for setting the log storage methods.
There are 5 Type of Action that we can use:
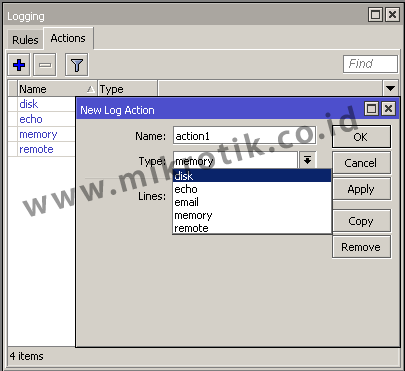
1. The Disk Type
With this type of logs will be stored as text files and are saved in the system storage router itself. We can always set the current log file name is stored in the File Name parameter. Can also set how many lines of the log file that is stored in each of his, could set the parameters of Lines per file.
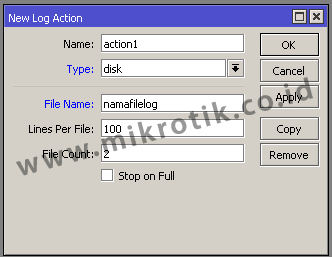
The log file can then be downloaded from the Files menu router and can be opened with a text editor on your PC
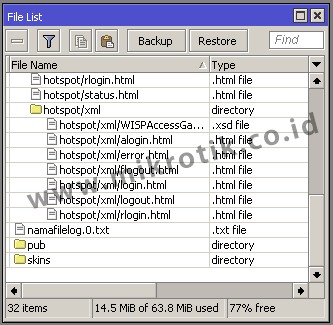
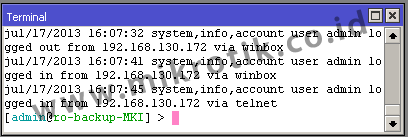
2. Type Echo
By using this type of router log will be displayed at the New Terminal (Winbox) or when we use the remote CLI (direct console)
3. Type email
Logs will be sent to the email that we have set. In order to function then we have to do before setting smtp server that will be used in the menu / tool e-mail
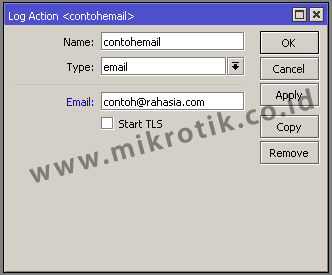
How often will the same as the email delivery Router how often the update log. Our advice, do not use public email services (like Yahoo or Gmail) because when sending emails too often public email services usually will consider it as spam.
4. The Memory Type
Logs will be stored in RAM Routers and can take a look at the log menu. Because only the logs are stored in RAM will be lost / can not read anymore after rebooting the router.
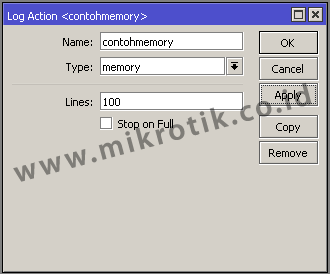
5. Type Remote
Logs will be sent to any device that runs the syslog server. We live designate the machine running the syslog server by entering the IP address.
If action has been created the next step we have to create a log rules.
Rules tab (/ system logging rules)
On the tab this rule we can make the topic or what services will we noted in the log. So that we can observe a process or service is more specific.
There are many services in our router and the new rules is that we make, we can specify one or more topic that we will record in the log.
The following example we will record all webproxy process is simple (! Debug).
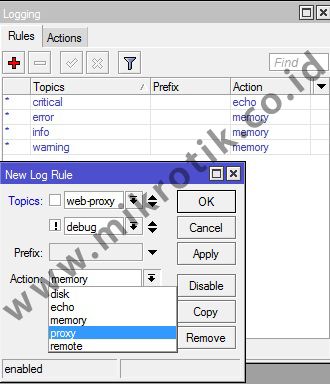
Topic! Debug is optional. This means that no topic! Debug logging webproxy will also keep running. ! Debug log is used to keep the display is not too detailed. By default if we specify a logging topic, there is a process of detailed information that occurs on a machine that sometimes even confusing.
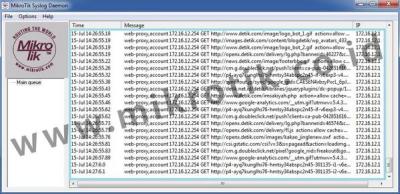
Example when logging topic WebProxy (! Debug) with remote action so that the log will be sent to the machine (PC) that runs the syslog server (172.16.1.254) with a simple syslog application of Mikrotik for Windows named MTSyslog.
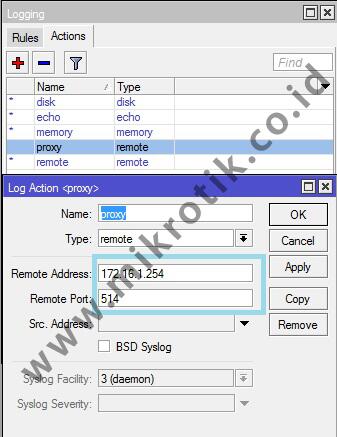
The following figure shows the log display is seen at the application MTSyslog
MTSyslog application can be downloaded free of charge here .
By using this logging function we do not need to observe the processes that occur on the router continuously at all times. We simply view the results of the record (log) of existing processes to see what is going on as long as you do not observe the router directly.
http://freakscontent.blogspot.com/